Ten revolutionary AI-powered weapons
- Problem: “The Evolving Landscape of Modern Warfare” Warfare is transforming in ways never witnessed before in history. The era of tank, infantry, and aerial bombers is slowly coming to an end, and the new age of warfare is taking over, this time with the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Governments and military organizations are racing to develop technologies that can leverage AI to redefine strategies, reduce human risks, and maximize operational efficiency. But with great innovation comes great responsibility, as AI-driven weapons also raise ethical dilemmas and geopolitical challenges.
- Agitation: “Why You Should Care About AI in Warfare” Whether you’re a defense strategist, a tech enthusiast, or simply a concerned citizen, understanding how AI is reshaping warfare is crucial. The stakes are incredibly high. AI-powered weapons promise to enhance military capabilities, but they also increase the risks of misuse and accidental escalation. Nations are building arsenals that could alter global power dynamics. With these developments, it’s vital to stay informed about the capabilities, use cases, and potential consequences of AI-driven weaponry.
Solution: 10 Revolutionary AI-Powered Weapons Changing the Game
This article discusses ten revolutionary AI-powered weapons that redefine modern warfare. We will get our hands dirty in their functionalities, real-world applications, and the implications they carry for world security.
Autonomous Drones
What they are:
Autonomous drones are UAVs that are fitted with AI algorithms that allow them to fly and operate without human intervention. They can navigate, identify targets, and execute missions on their own.
Case Study:
In 2020, during the Libyan civil war, Turkish-made KARGU-2 drones were reportedly used to autonomously target enemy combatants. The drones used facial recognition and other AI tools to engage targets without requiring commands from operators.
Why It Matters:
Autonomous drones minimize the requirement for on-ground personnel and offer tactical advantages in reconnaissance, surveillance, and combat missions. However, deployment of autonomous drones raises questions regarding accountability and potential errors in identifying targets.
AI-Based Missile Systems
What They Are:
AI-based missile systems use machine learning algorithms to enhance precision, adapt to changing environments, and evade countermeasures.
Case Study:
Russia’s “Poseidon” nuclear-capable torpedo is fitted with AI to travel underwater autonomously. It can avoid traditional defense systems and strike coastal targets accurately, even in difficult environments.
Why It Matters:
By introducing AI, missile systems become more intelligent and challenging to intercept. However, they also increase the dangers of accidental effects, especially in high-stakes nuclear games.
Swarm Robotics
What They Are:
In swarm robotics, essentially, numerous AI-enabled robots or drones are placed in the environment and work collaboratively, mimicking similar behaviors found in nature- say bees or ants.
Case Study
In 2017, the U.S. Department of Defense tested a swarm of 103 Perdix drones, highlighting the aspect of collective decision-making, adaptive behavior, and reconfiguration in case individual units were lost.
Why It Matters:
Swarm systems tend to overwhelm all traditional defense systems with their volume and flexibility. They are exceptionally effective in electronic warfare, intelligence gathering, and crowd control. However, that may create a new arms race in swarm technology.
AI-Driven Cyber Weapons
What They Are:
AI-based cyber weapons employ autonomous systems in the detection of vulnerabilities in adversary systems, providing faster and more accurate cyber attacks.
Case Study:
The 2021 Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack was a demonstration of how advanced AI tools could be used for sophisticated cyber operations. Not directly a military initiative, the attack showed how AI-enhanced malware can disrupt critical infrastructure.
Why It Matters:
Cyber weapons blur the lines between civilian and military targets, making them especially dangerous. They are difficult to attribute and counter, which increases the risk of escalation in cyber conflicts.
AI-Enhanced Surveillance Systems
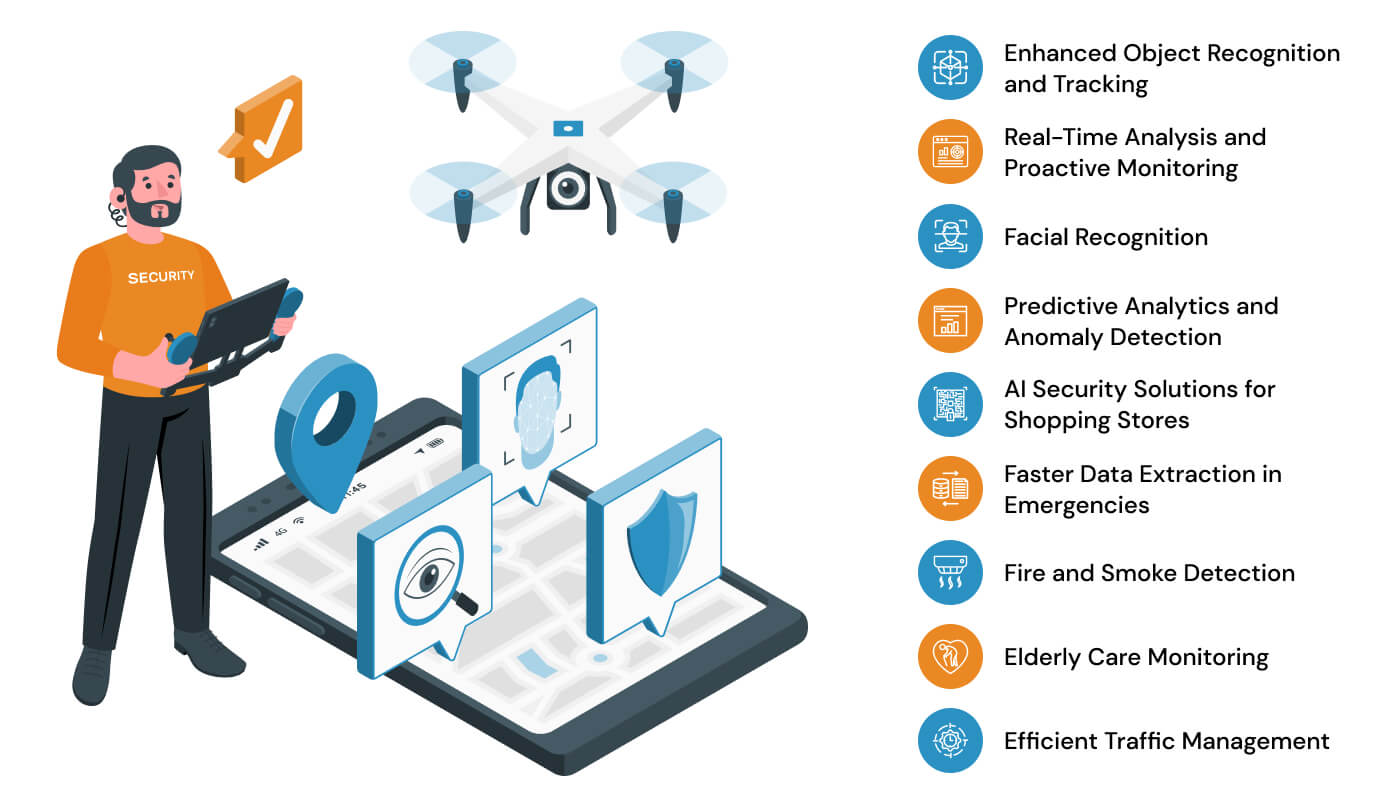
What They Are:
AI surveillance systems use facial recognition, object detection, and pattern analysis to monitor and analyze large datasets in real time.
Case Study:
China’s military uses AI-driven surveillance to monitor activities along its borders and within the country. The integration of AI into its social credit system also provides insights into how this technology could be weaponized for control and suppression.
Why It Matters:
While AI surveillance may strengthen national security, it is also a major threat to privacy and civil liberties. Its weaponization in war zones could be the greatest social control ever known.
Autonomous Ground Vehicles (AGVs)
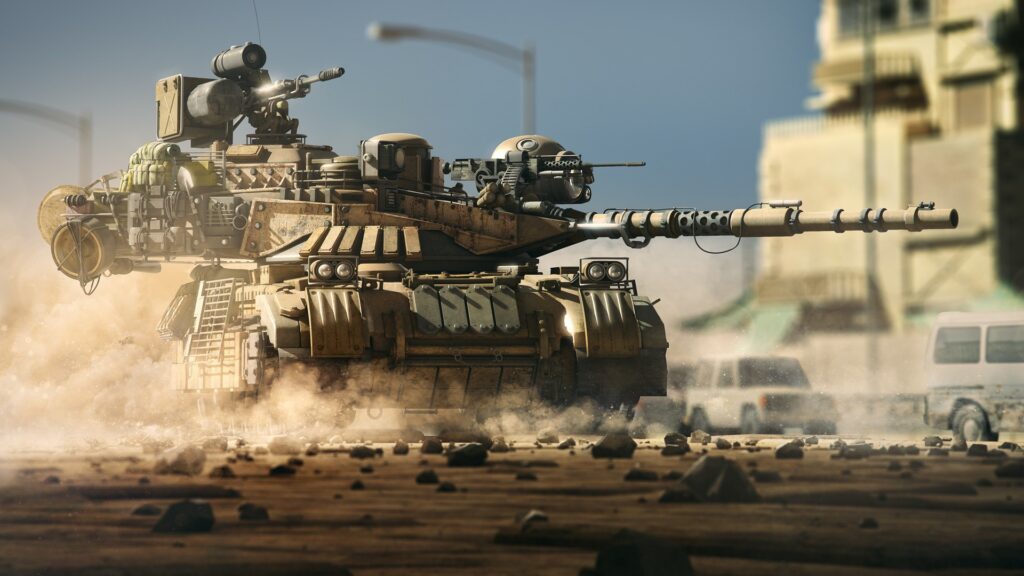

What They Are:
AGVs are AI-powered robotic vehicles designed for military applications such as logistics, reconnaissance, and combat.
Russia’s “Uran-9” combat vehicle has the capacity for autonomous navigation and targeting. In Syria, it showcased potential but also shortcomings of AGVs in the heat of actual warfare.
Why It Matters:
AGVs can conduct dangerous missions without losing human lives. Yet, it still fails when unpredicted circumstances occur as witnessed in field testing when it malfunctions due to technical failure.
AI-Integrated Submarines
What They Are:
AI-fitted submarines help improve the process of navigation while underwater, the identification of threats, and the planning of the mission.
Case Study:
The U.S. Navy’s Orca Extra-Large Unmanned Undersea Vehicle (XLUUV) is designed to operate autonomously for extended missions, including surveillance and mine-laying.
Why It Matters:
AI submarines extend the reach and efficiency of naval forces. Their autonomous nature allows for prolonged operations in hostile or contested waters. However, they also complicate traditional naval strategies and deterrence.
AI in Electronic Warfare
What They Are:
AI improves electronic warfare systems by automatically detecting, analyzing, and disrupting enemy communications and radar systems.
Case Study:
Israel’s “Scorpius” electronic warfare system uses AI to detect and neutralize multiple threats at the same time. It can target aircraft, drones, and missiles with precision.
Why It Matters:
AI-driven electronic warfare gives a decisive edge in modern conflicts. However, its potential for collateral damage—such as disrupting civilian communication networks—raises ethical concerns.
Predictive AI Systems
What They Are:
Predictive AI predicts enemy action, optimizes resource allocation, and anticipates threats using data analytics and machine learning.
Case Study
The US military’s Project Maven uses AI to analyze drone footage and identify potential targets. It significantly reduces the time needed for intelligence analysis.
Why It Matters
Predictive AI enhances decision-making and operational efficiency. But if there are errors in the underlying data or algorithms, the system might produce errors if relied upon too heavily.
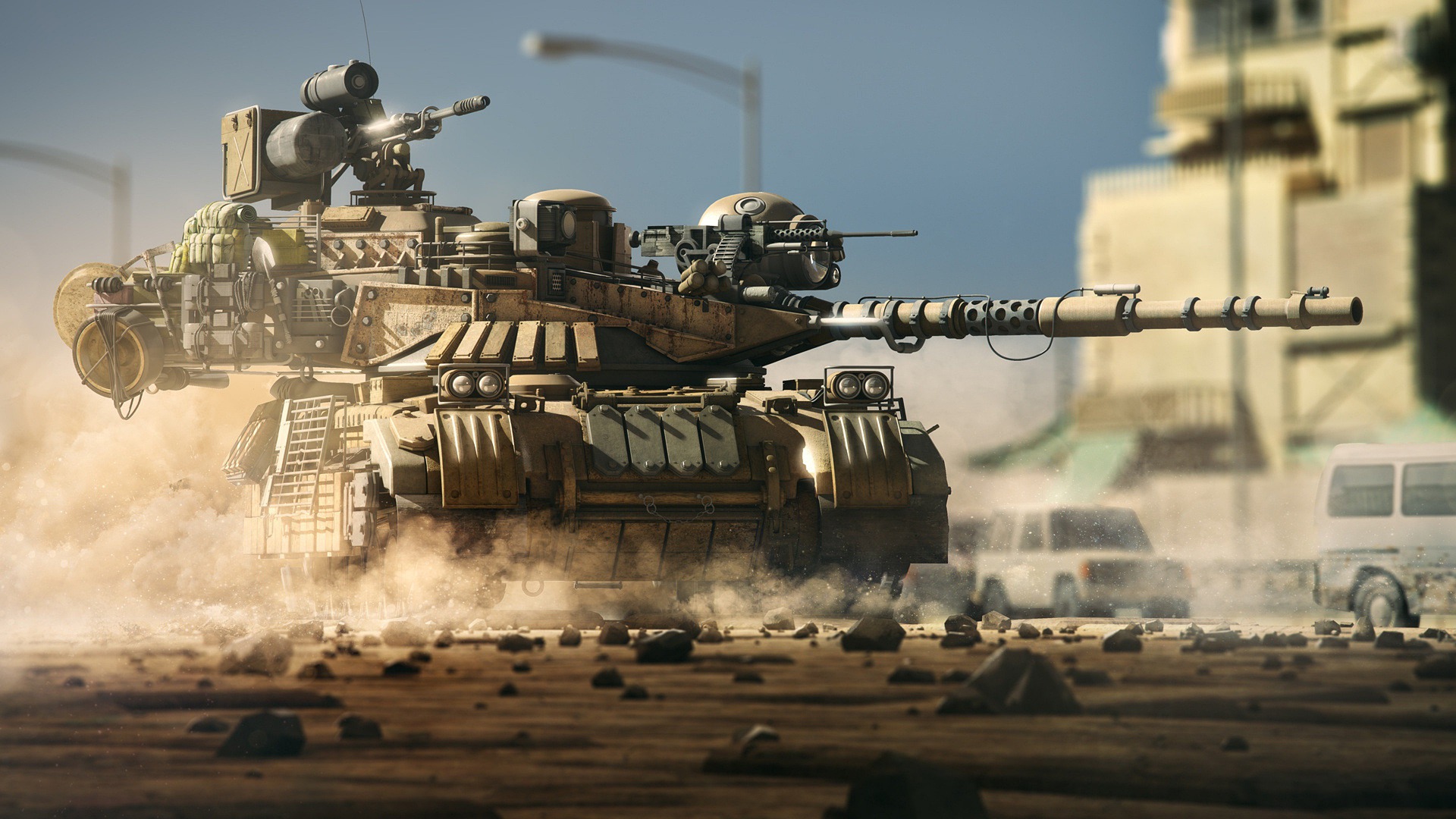
Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems (LAWS)
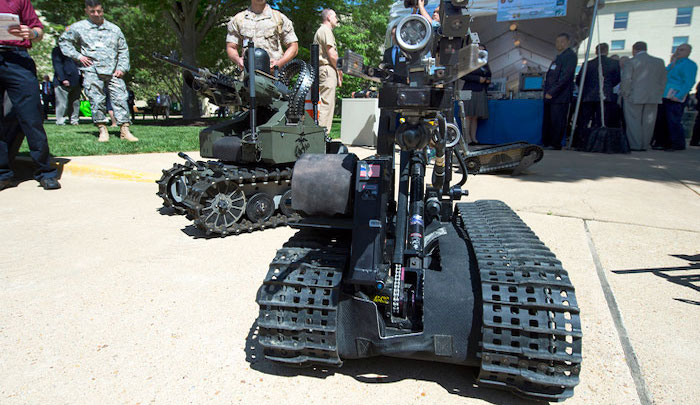

What They Are:
LAWS are fully autonomous systems capable of selecting and engaging targets without human input.
Case Study:
South Korea’s Samsung SGR-A1 sentry gun, deployed in the Demilitarized Zone, uses AI to identify and engage targets. While it currently requires human authorization to fire, it showcases the potential for fully autonomous deployment.
Why It Matters:
Conclusion
LAWS can change the face of warfare by making humans completely absent from the battlefield. But at the same time, they bring forth deep ethical and legal issues of accountability and human oversight.
AI is transforming the landscape of modern warfare in many ways. Autonomous drones, predictive analytics, and many more are some of the unprecedented capabilities with complex challenges that they bring with them. It promises to make military operations much more efficient and less risky for human soldiers. However, misuse and unintended consequences cannot be ruled out.
As nations continue to invest in AI-driven weapons, it is critical to create an international dialogue over regulations and ethical guidelines. It will depend not only on how much we are able to innovate but also on our collective capacity to manage and control the implications of such advancements.
The understanding of these revolutionary weapons can be used to prepare better for the challenges and opportunities they bring to global security.
What are ultra-concentrated energy weapons, and how do they work?
Ultra-concentrated energy weapons, such as high-energy lasers (HEL), use advanced technology to emit powerful laser beams. These lasers can cut through materials with high precision and can disable drones, missiles, and even melt armor1. AI optimizes energy output and targeting, allowing these weapons to be deployed from significant distances with minimal collateral damage.
How do gravitational wave weapons differ from traditional explosives, and what role does AI play in their operation?
Gravitational wave weapons manipulate gravitational waves—ripples in the fabric of spacetime—to disrupt molecular structures, causing buildings or entire cities to collapse without visible explosions. Unlike traditional explosives that destroy from the outside, these weapons target the internal structure of materials1. AI fine-tunes the wavelength and intensity of gravitational waves for precise targeting, minimizing civilian casualties.
What are nanobots, and how can they be used in covert warfare?
Nanobots are tiny robots that operate at the molecular level. While current research explores their use in medicine, AI can weaponize these nanobots to infiltrate enemy systems or biological entities without detection1. Swarms of nanobots can silently disable critical infrastructure or incapacitate enemy combatants from within, adapting to avoid countermeasures and making them nearly impossible to eliminate
I hope, this was helpfull to all !





Leave a Reply